Switch is an electrical component that can make or break an electrical circuit. It has conductive pieces (often metal) called contacts or terminal that touch to close (make) or open (break) a connection.
A pair of contacts is closed (switched on) when current can flow from one contact to other. When the contacts are separated by an air gap, they are open (switched off) and no current can flow between them.

Switches used for home wiring are mechnical switches and have an internal arrangement as shown below.

Electromechanical switches like relay are used for specialized operations.
Note: The representation shown below is the technical representation (used in diagrams) followed by some actual switches used.
Technically, based on the number of contacts, switches can be classified as:
- SPST (Single pole, single throw)
It is a simple on-off switch. The two terminals are either connected together or disconnected from each other.
For Ex: light switch in homes.
![]()

- SPDT (Single pole, double throw)
It has a common contact C (COM) connected to either of two other contacts A or B.
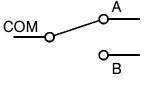

- SPCO (Single pole, centre off)
Equivalent to SPDT switch, only that it has a centre off position.


- DPST (Double pole, single throw)
Equivalent to two SPST switches controlled by a single mechanism.


- DPDT (Double pole, double throw)
Equivalent to two SPDT switches controlled simultaneoulsy.


A is connected to either B or C, D is connected to either E or F.
- DPCO (Double pole, centre off)
Equivalent to a DPDT switch, it has a stable off position in the centre.

Switches derived from above are switches are
- Push-to-make
A push-to-make switch returns to its normally open (off) position when you release the button, this is shown by the brackets around ON.
For Ex: Doorbell switch.
![]()
![]()
- Push-to-break
A push-to-break switch returns to its closed (on) position when you release the button.
![]()

Source: Wikipedia

No comments:
Post a Comment